Future Simple Tense (Will vs Going To) – Rules, Uses & Examples
What is the Future Simple Tense?
The Future Simple Tense is used to talk about actions or events that will happen in the future.
In English, we mainly use two forms to talk about the future:
Will
Going to
Both are correct, but they are used in different situations.
Understanding the difference between will and going to helps you sound clear and natural in English.
Future Simple with “Will”
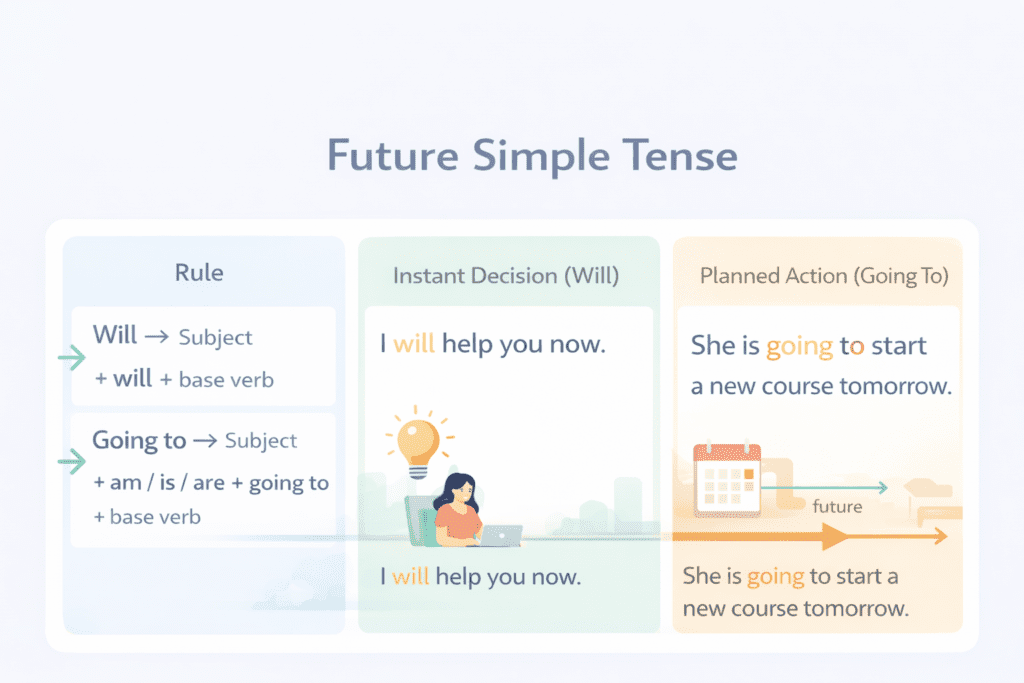
Structure (Will)
Subject + will + base form of verb
Examples:
I will learn English.
She will call you later.
They will attend the meeting.
👉 “Will” is the same for all subjects.
Uses of “Will”
1. Instant Decisions
Use will when you decide to do something at the moment of speaking.
Examples:
I’m tired. I will rest now.
The phone is ringing. I will answer it.
It’s hot. I will open the window.
2. Promises
Use will to make promises.
Examples:
I will help you with your homework.
She will support you.
We will never forget this day.
3. Offers and Requests
Use will when offering or asking for help.
Examples:
I will carry your bag.
Will you help me, please?
Will you call me later?
4. Predictions (Opinion-Based)
Use will for predictions based on personal opinion, not evidence.
Examples:
I think it will rain today.
She will become a good speaker.
This movie will be interesting.
Future Simple with “Going To”
Structure (Going To)
Subject + am / is / are + going to + base form of verb
Examples:
I am going to learn English.
She is going to start a new job.
They are going to travel next month.
Uses of “Going To”
1. Planned Actions
Use going to for actions that were planned before speaking.
Examples:
I am going to join an English course.
She is going to meet her teacher.
We are going to visit our relatives.
2. Strong Evidence-Based Predictions
Use going to when you see clear signs or evidence.
Examples:
Look at the clouds. It is going to rain.
He is driving fast. He is going to crash.
She looks tired. She is going to fall asleep.
Will vs Going To – Key Differences
| Will | Going To |
|---|---|
| Instant decision | Planned decision |
| Promise / offer | Already decided plan |
| Opinion-based prediction | Evidence-based prediction |
| “I will help you” | “I am going to help you” |
Example Comparison
I will study tonight. (decision made now)
I am going to study tonight. (plan made earlier)
Sentence Forms
Affirmative Sentences
Will:
I will practice English daily.
She will complete the lesson.
Going To:
I am going to practice English daily.
She is going to complete the lesson.
Negative Sentences
Will:
Subject + will not + verb
I will not miss the class.
She will not stop learning.
Short form: won’t
Going To:
Subject + am / is / are + not + going to + verb
I am not going to attend today.
They are not going to travel now.
Interrogative Sentences (Questions)
Will:
Will you join the course?
Will she call you?
Going To:
Are you going to join the course?
Is she going to call you?
Wh-Questions
What will you do tomorrow?
Where are you going to travel?
When will she start learning English?
Common Time Expressions Used
tomorrow
next week / month / year
soon
in the future
Examples:
I will start tomorrow.
She is going to appear next week.
We will meet soon.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
❌ I will going to learn English.
✅ I will learn English.
✅ I am going to learn English.
❌ She going to start tomorrow.
✅ She is going to start tomorrow.
❌ Will you going to attend?
✅ Will you attend?
✅ Are you going to attend?
More Examples for Practice
I will improve my grammar.
She is going to practice speaking daily.
We will achieve our goals.
They are going to build confidence in English.
Quick Summary
Will → instant decisions, promises, opinions
Going to → plans, strong evidence
Both talk about the future
Choose based on situation, not preference
✅ Tip for Learners
If the plan is already decided, use going to.
If the decision is made now, use will.
