Phrases and Clauses – Definition, Types & Examples
What Are Phrases and Clauses in English?
In English grammar, phrases and clauses are groups of words that help us build sentences.
Many learners get confused between phrases and clauses, but the difference is actually simple:
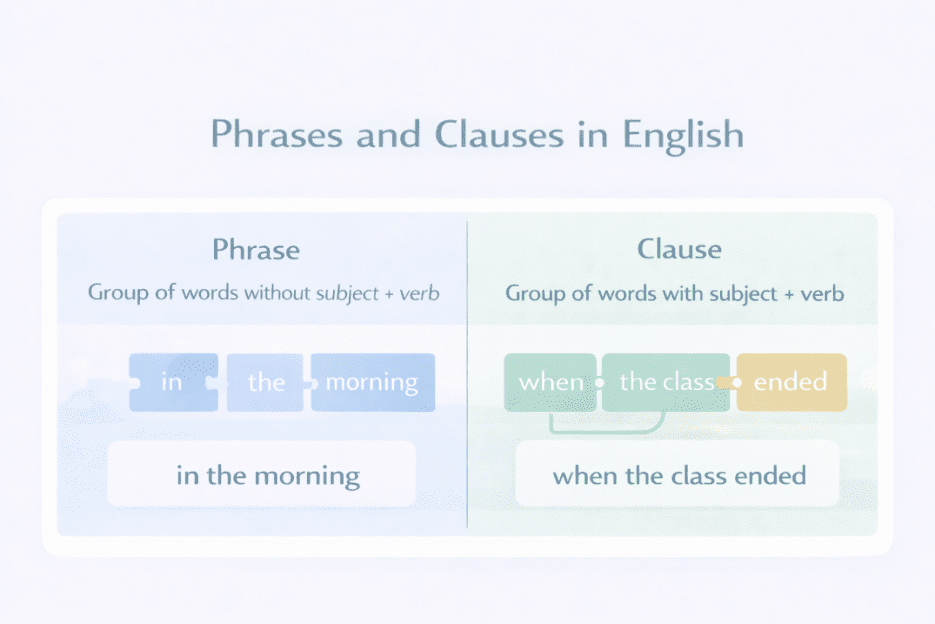
A phrase does not have a subject and a verb together
A clause does have a subject and a verb
Understanding phrases and clauses will help you:
Form correct sentences
Identify sentence structure easily
Avoid incomplete or incorrect sentences
What is a Phrase?
A phrase is a group of words that:
Works together as a unit
Does not contain both a subject and a verb
Does not express a complete idea
A phrase cannot stand alone as a sentence.
Examples of Phrases
in the morning
very happy
under the table
learning English
a beautiful place
❌ In the morning. (not a complete sentence)
❌ Very happy. (missing subject and verb)
Types of Phrases in English
1. Noun Phrase
A noun phrase has a noun as the main word.
Structure:
Determiner + adjective(s) + noun
Examples:
a smart student
the English language
my best friend
those online classes
2. Verb Phrase
A verb phrase contains a main verb and sometimes helping verbs.
Examples:
is learning
has completed
will be attending
was practicing
3. Prepositional Phrase
A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with a noun.
Examples:
in the room
on the table
under the bridge
at night
4. Adjective Phrase
An adjective phrase describes a noun.
Examples:
very beautiful
full of confidence
extremely useful
5. Adverb Phrase
An adverb phrase describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb.
Examples:
very slowly
quite well
too quickly
What is a Clause?
A clause is a group of words that:
Has a subject
Has a verb
May or may not express a complete idea
Unlike phrases, clauses always contain a subject and a verb.
Examples of Clauses
She is learning English
They are practicing daily
Because he was tired
When the class ended
Types of Clauses in English
1. Independent Clause
An independent clause:
Has a subject and a verb
Expresses a complete idea
Can stand alone as a sentence
Examples:
I am learning English.
She works in an office.
They completed the lesson.
2. Dependent Clause (Subordinate Clause)
A dependent clause:
Has a subject and a verb
Does not express a complete idea
Cannot stand alone
It usually begins with words like:
because, although, when, if, while, since, before, after, that
Examples:
because she wants to improve
when the class ended
although he was tired
if you practice daily
❌ Because she wants to improve.
✅ She is learning English because she wants to improve.
Types of Dependent Clauses
1. Noun Clause
A noun clause acts like a noun in a sentence.
Examples:
I know that she is learning English.
What he said was true.
She believes that practice is important.
2. Adjective Clause (Relative Clause)
An adjective clause describes a noun.
It often starts with:
who, which, that, whom, whose
Examples:
The student who practices daily improves faster.
This is the book that I like.
She met a teacher who helped her.
3. Adverb Clause
An adverb clause gives more information about time, reason, condition, contrast, etc.
Examples:
I stayed home because it was raining.
She will succeed if she practices daily.
He continued studying although he was tired.
Phrase vs Clause – Key Differences
| Phrase | Clause |
|---|---|
| No subject + verb together | Has subject + verb |
| Incomplete idea | May be complete or incomplete |
| Cannot stand alone | Independent clause can |
| “in the morning” | “when the morning came” |
Example Comparison
Phrase: in the evening
Clause: when the evening arrived
Common Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Because I was tired.
✅ I went to bed because I was tired.
❌ Running in the park.
✅ Running in the park is fun.
❌ She learning English.
✅ She is learning English.
Practice Examples
Identify whether it is a phrase or a clause:
in the classroom → Phrase
she is learning English → Clause
because he was late → Clause
very useful → Phrase
after the class ended → Clause
Why Phrases and Clauses Are Important
Help build correct sentences
Improve writing clarity
Prevent sentence fragments
Make spoken English more natural
Quick Summary
A phrase does not have both a subject and a verb
A clause has a subject and a verb
Clauses can be independent or dependent
Sentences are built using phrases and clauses together
✅ Tip for Learners
If a group of words feels incomplete, ask:
Does it have both a subject and a verb?
If yes → it’s a clause
If no → it’s a phrase
