Adverbs – Types, Rules & Examples
What is an Adverb?
An adverb is a word that adds more information about:
a verb
an adjective
another adverb
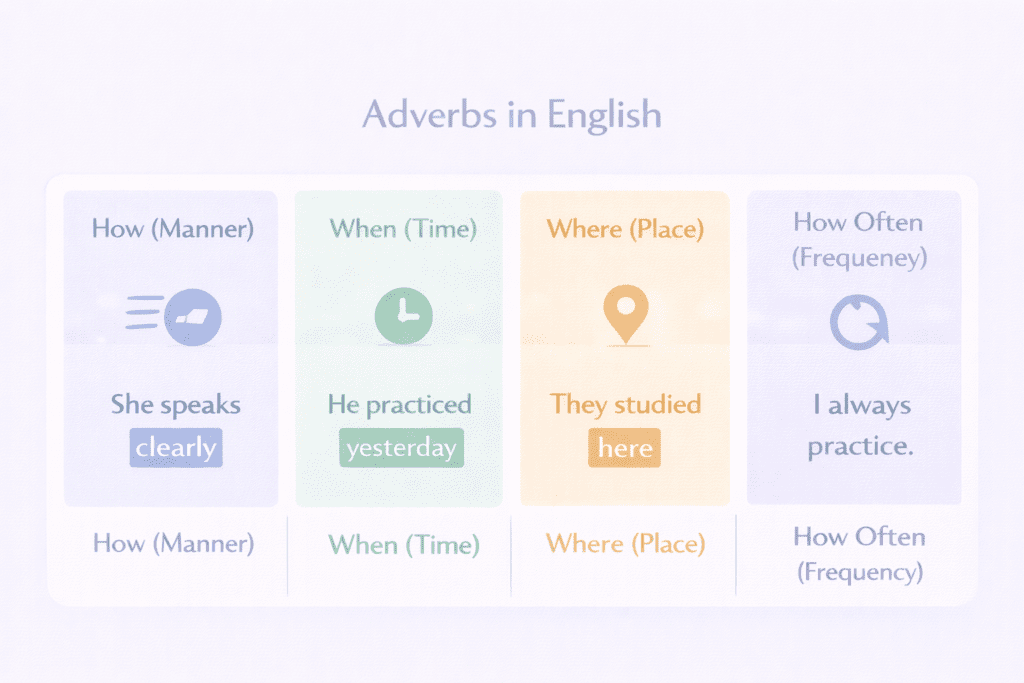
In simple words, adverbs tell us:
How something happens
When it happens
Where it happens
How often it happens
Examples of Adverbs
quickly
slowly
yesterday
here
always
Examples in sentences:
She speaks English fluently.
I practiced yesterday.
They are studying here.
He always arrives on time.
Why Adverbs Are Important
Adverbs help us:
Give clear details
Express time, place, manner, and frequency
Make sentences more natural and complete
Compare:
❌ She speaks English.
✅ She speaks English clearly.
Types of Adverbs in English
Adverbs are divided into different types based on what they describe.
1. Adverbs of Manner (How?)
What are Adverbs of Manner?
Adverbs of manner tell us how an action happens.
Most adverbs of manner end in -ly.
Examples
slowly
clearly
carefully
confidently
Examples in sentences:
She speaks English clearly.
He completed the task carefully.
They worked hard.
(Hard is an adverb without -ly)
2. Adverbs of Time (When?)
What are Adverbs of Time?
Adverbs of time tell us when an action happens.
Examples
today
yesterday
now
soon
later
Examples in sentences:
I practiced English yesterday.
She will join the class soon.
They are studying now.
3. Adverbs of Place (Where?)
What are Adverbs of Place?
Adverbs of place tell us where an action happens.
Examples
here
there
inside
outside
everywhere
Examples in sentences:
Please sit here.
They searched everywhere.
The teacher is waiting outside.
4. Adverbs of Frequency (How Often?)
What are Adverbs of Frequency?
Adverbs of frequency tell us how often something happens.
Common Adverbs of Frequency
always
usually
often
sometimes
rarely
never
Examples in Sentences
I always practice English.
She often watches English videos.
He never misses class.
Position Rule (Important)
Adverbs of frequency usually come:
Before the main verb
After “be” verbs
✅ She always practices daily.
✅ He is often late.
5. Adverbs of Degree (How Much?)
What are Adverbs of Degree?
Adverbs of degree tell us how much or to what extent.
Examples
very
too
quite
almost
enough
Examples in sentences:
English is very important.
She is too tired today.
The lesson was quite easy.
Position of Adverbs in a Sentence
Adverbs can appear:
At the beginning
In the middle
At the end
Examples
Yesterday, I practiced English.
She quickly understood the lesson.
He speaks English well.
Adverbs vs Adjectives (Common Confusion)
| Adjective | Adverb |
|---|---|
| good | well |
| quick | quickly |
| slow | slowly |
| careful | carefully |
Examples
❌ She speaks English good.
✅ She speaks English well.
❌ He runs quick.
✅ He runs quickly.
Common Adverb Mistakes to Avoid
❌ She speaks very fluent.
✅ She speaks very fluently.
❌ He did the work careless.
✅ He did the work carelessly.
❌ I am always go there.
✅ I always go there.
How to Identify an Adverb
Ask these questions:
How?
When?
Where?
How often?
How much?
If the word answers one of these, it is likely an adverb.
Practice Examples
Identify the adverb:
She speaks clearly.
I studied yesterday.
They work together.
He always arrives early.
Why Learning Adverbs Is Important
Improves sentence clarity
Adds useful details
Makes speech sound natural
Helps express habits and routines
Quick Summary
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs
They tell us how, when, where, how often
There are different types of adverbs
Correct placement is important
✅ Tip for Learners
When you learn a verb, try to learn one adverb with it.
Example:
speak → speak clearly
work → work hard
This will improve fluency faster.
