Past Perfect Tense – Rules, Uses & Examples
What is the Past Perfect Tense?
The Past Perfect Tense is used to talk about an action that was completed before another action in the past.
In simple words, this tense helps us show which action happened first when we are talking about two past events.
Think of it as the “past before the past.”
Structure of the Past Perfect Tense
The basic structure is:
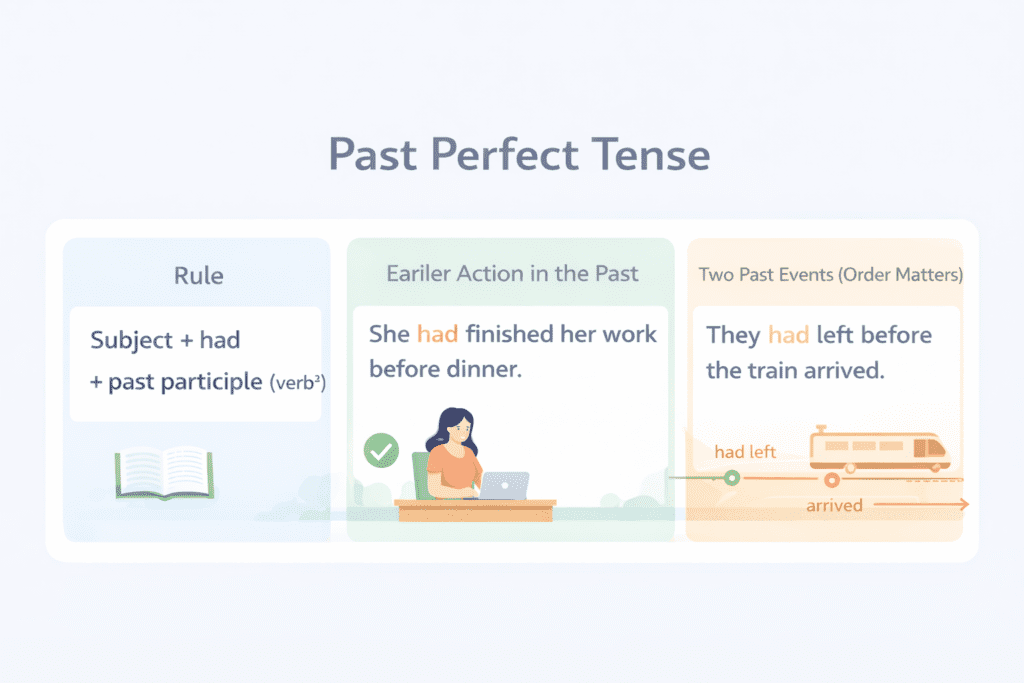
Subject + had + past participle (verb³)
Examples:
I had finished my work before dinner.
She had left the office when I called.
They had reached home before it started raining.
👉 “Had” is used for all subjects.
Uses of the Past Perfect Tense
1. One Action Completed Before Another Past Action
This is the most common use of the past perfect tense.
The earlier action uses past perfect,
The later action uses past simple.
Examples:
I had completed my homework before I went out.
She had cooked dinner before guests arrived.
They had booked the tickets before the prices increased.
2. To Show Cause and Effect in the Past
Use the past perfect tense to explain why something happened in the past.
Examples:
He was tired because he had worked all day.
She missed the train because she had woken up late.
We were happy because we had finished the project early.
3. Reported Speech
The past perfect tense is often used in reported speech when talking about earlier actions.
Examples:
She said that she had completed the task.
He told me that he had already eaten.
They said they had never visited India before.
4. With Time Expressions Like “Before” and “After”
Although before and after already show time order, the past perfect tense is used to make the meaning very clear.
Examples:
I had locked the door before I left.
She had finished the exam before the bell rang.
After we had eaten, we went for a walk.
Sentence Forms
Affirmative Sentences
Subject + had + past participle
Examples:
I had learned English basics.
She had joined the course earlier.
They had completed the lesson.
Negative Sentences
Subject + had not + past participle
Examples:
I had not seen the movie before.
She had not prepared well.
They had not informed us earlier.
Short form:
had not → hadn’t
Interrogative Sentences (Questions)
Had + subject + past participle?
Examples:
Had you finished the work?
Had she left when you arrived?
Had they met him earlier?
Wh-Questions
Wh-word + had + subject + past participle?
Examples:
Why had she left early?
What had you decided?
Where had they gone?
Common Time Expressions Used
before
after
already
just
never
by the time
Examples:
By the time we arrived, the show had started.
She had already completed the task.
He had never spoken English before.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
❌ I had went to office before lunch.
✅ I had gone to office before lunch.
❌ She had finish the work.
✅ She had finished the work.
❌ Had you did the homework?
✅ Had you done the homework?
Past Simple vs Past Perfect
| Past Simple | Past Perfect |
|---|---|
| Later past action | Earlier past action |
| “I reached home” | “I had reached home” |
| Time is clear | Order is emphasized |
Example Comparison:
I reached the station. The train left. ❌ (unclear)
I reached the station, but the train had left. ✅ (clear)
More Examples for Practice
I had practiced grammar before the test.
She had improved her speaking skills.
We had planned everything in advance.
They had completed all lessons earlier.
Quick Summary
Used for actions completed before another past action
Structure: had + verb³
Helps show sequence of past events
Often used with before, after, by the time
✅ Tip for Learners
Whenever you talk about two past actions and want to show which one happened first, use the past perfect tense.