Prepositions – Types, Rules & Usage
What is a Preposition?
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between:
a noun or pronoun
and another word in the sentence
Prepositions usually tell us:
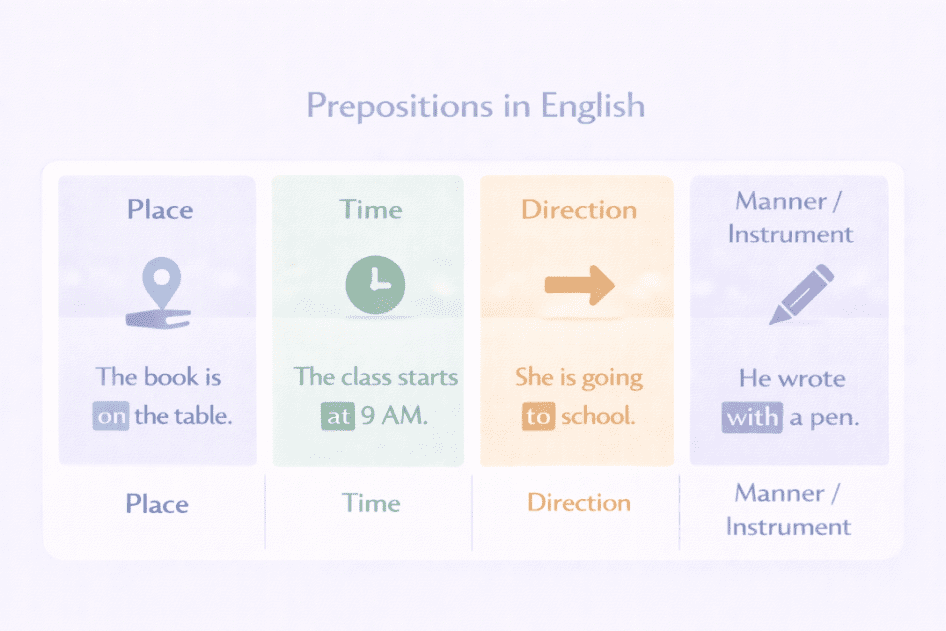
Where something is (place)
When something happens (time)
How something moves (direction)
Relationship between objects
Examples of Prepositions
in
on
at
under
before
after
Examples in sentences:
The book is on the table.
She studies at night.
He arrived after the class.
Why Prepositions Are Important
Prepositions help us:
Give clear meaning to sentences
Avoid confusion
Speak and write more accurately
Compare:
❌ The book is the table.
✅ The book is on the table.
Common Prepositions in English
Some very common prepositions are:
in, on, at, to, from, for, with, about, by, under, over, between, among
Types of Prepositions
Prepositions can be grouped based on how they are used.
1. Prepositions of Place
What are Prepositions of Place?
They show where something or someone is.
Common Prepositions of Place
in
on
at
under
over
behind
between
among
Examples in Sentences
The keys are on the table.
She is in the room.
The cat is under the chair.
He stood between two friends.
2. Prepositions of Time
What are Prepositions of Time?
They show when something happens.
Common Prepositions of Time
at
on
in
before
after
during
Examples in Sentences
The class starts at 9 AM.
I study in the evening.
We met on Monday.
She left after lunch.
IN – ON – AT (Quick Rule)
| Preposition | Used for |
|---|---|
| in | months, years, long periods |
| on | days, dates |
| at | exact time |
Examples:
in June
on Monday
at 7 PM
3. Prepositions of Direction
What are Prepositions of Direction?
They show movement from one place to another.
Common Prepositions of Direction
to
into
onto
towards
from
Examples in Sentences
She is going to school.
He walked into the room.
The cat jumped onto the table.
They moved towards the exit.
4. Prepositions of Manner / Instrument
What are Prepositions of Manner or Instrument?
They show how something is done or with what.
Common Prepositions
by
with
using
Examples in Sentences
She came by bus.
He cut the paper with scissors.
I wrote the email using my phone.
5. Prepositions of Cause / Reason
What are Prepositions of Cause?
They show why something happens.
Examples
because of
due to
owing to
Examples in sentences:
The match was canceled because of rain.
The delay was due to traffic.
Position of Prepositions in a Sentence
Prepositions usually come:
Before a noun or pronoun
✅ She is sitting on the chair.
✅ He spoke about the problem.
Ending a Sentence with a Preposition
In modern English, this is acceptable.
This is the book I told you about.
Who are you talking to?
Common Preposition Mistakes to Avoid
❌ She is married with him.
✅ She is married to him.
❌ I am good in English.
✅ I am good at English.
❌ He discussed about the issue.
✅ He discussed the issue.
(Discuss does not need a preposition)
Prepositions vs Conjunctions (Quick Note)
Preposition → followed by a noun/pronoun
Conjunction → joins clauses
Example:
I stayed home because of rain. (preposition)
I stayed home because it was raining. (conjunction)
Practice Examples
Fill in the blanks:
The book is ___ the table. (on)
She arrived ___ 8 PM. (at)
We met ___ Monday. (on)
He walked ___ the room. (into)
Why Learning Prepositions Is Important
Avoids common grammar errors
Improves clarity
Helps with fluent speaking
Essential for correct sentence meaning
Quick Summary
Prepositions show relationship
They tell us place, time, direction, manner
Always followed by a noun or pronoun
Small words, but very important
✅ Tip for Learners
Prepositions are best learned with examples, not rules alone.
Example:
good at
interested in
afraid of
